Second Place: C02 Crew

“CO2 Crew blends the Astrodome's scale with efficiency, proposing a new community above the surrounding parking lots for sustenance, walkability, and resilience.”
CO2 Crew blends the Astrodome's scale with efficiency, proposing a new community above the surrounding parking lots for sustenance, walkability, and resilience. A carbon-neutral platform reduces the heat-island effect, boostng density, diversity, and activity. Innovative zero-carbon buildings maximize solar gain and offset energy with solar arrays. The Astrodome is repurposed into a terraced urban farm, education center, and community farmers market addressing food security within Houston. Removing the existing roof unveils the elegant lamella structure transforming the stadium into an open-air pavilion for farming. While the terraced seating becomes 4.5 acres of urban farmland with vertcal hydroponics, the lamella structure harnesses solar energy through a sun-tracking array. The Education Center Pyramid emerges from the interplay of ley lines, connecting prominent Houston landmarks to its center and informing the pyramid's geometry. The Center includes classrooms, research and exhibition spaces, a library, bike storage, two theaters, a café, and a restaurant. The public plaza at the heart of the Education Centre is a communal hub with a thriving farmers' market, music, and a lively space for interaction and dialogue. Astrodome's transformation honors its history, reimagines the present, and shapes a vibrant future while redefining urban landscape and community experience.
TEAM POSTER FULL SUMMARY PRESENTATION video
VIEW PREVIOUS LDSD WINNERS
In the Media:  Houston Chronical | October 29, 2023
Houston Chronical | October 29, 2023
Houston Astrodome reimagined in national architecture competition
2023 Teams | Houston Astrodome Model | Design Requirements | Analysis | Design Narrative | Contextual Information | Evaluation Criteria | Judges | Important Dates
The 2023 ASHRAE LowDown Showdown is here!
Sign up now and unleash your design and modeling skills, collaborate with project team members and showcase your innovative building design to conference attendees!
This year’s selection for the model building is an existing building – the one and only Houston Astrodome! The Astrodome, built in 1965 served as a sports arena for over three decades until 2000. It now sits in disrepair, despite multiple attempts to repurpose the building over the years.
That is the challenge! Teams will be asked to envision a new creative reuse of the Houston Astrodome to provide needed urban amenities and to do so within the constraints of reduced fossil fuel use and reduced carbon emissions. Teams will be given the freedom to think out of the box to determine how this voluminous, enclosed structure can bring meaningful activities and/or services to the Houston area.
Here’s your chance to join an integrated team that will compete for fun and prizes. Sign up today and create your own team or sign up as an individual participant and we will put you on a team! Bring your imagination and analytical skills to the party and design a facility that is durable, provides exceptional indoor air quality and minimizes energy use and carbon emissions from operations and materials.
The goal of the LowDown Showdown modeling competition is to engage participants in a collaborative and fun learning experience that explores new advances in building science, modeling, and technology. Teams are comprised of building analysts, designers, architects, engineers, and other participants. Teams will be responsible for creating the architectural design and a performance analysis model based on model building data. The teams may use any software or a combination of software to complete their projects.
Each team will create and submit a poster of their building design, complete the performance analysis model and results spreadsheet, and write a one-page narrative on project workflow. Teams will present their projects at the BPAC conference and be judged by a panel of industry experts who will select the winners.

-
Houston Astrodome Model
Download files
Design Requirements
✔️Program: Re-envisioning the functional use of the Astrodome is left to the imagination and initiative of the competition teams. The full interior and selected exterior (parking lot footprint) of the building is expected to be engaged. The development of concepts to be presented is expected to be at a level commensurate with the conceptual design phase of a project.
✔️Systems: Major building systems, including HVAC, lighting, site energy, enclosure revisions (as necessary) appropriate to the program proposal will be evaluated, described, and modeled.
✔️Carbon: The project will be designed to reduce carbon emissions both from building operations and from construction materials used for the rehabilitation. Operational carbon should be commensurate with that of a net-zero energy building. Emitted/embodied carbon will be representative of current best practices and include consideration of building mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems.
✔️Comfort: Intended comfort outcomes and design approaches will be documented to demonstrate that the project will provide thermal, visual, and acoustical comfort appropriate to the proposed space typologies informed by the current versions of the LEED and Green Globes certification standards, while demonstrating awareness of enhanced IEQ strategies in the WELL Standard.
✔️Indoor Air Quality: Intended IAQ design approaches and outcomes will be documented to demonstrate that the project incorporates innovative solutions to deliver exceptional indoor air quality, displaying an understanding of design strategies intended to improve occupant health and wellness.
✔️Durability: Design decisions will reflect a concern for a durable project that meets criteria established and presented by the design team. A hygrothermal analysis will be considered a plus; as will a plan for project deconstruction.
| return to top
Analysis
Design targets for the following elements will be clearly listed and compared with predicted project performance:
- Site EUI (kBtu/ft2 yr) [kWh/m2 yr]
- Source EUI (kBtu/ft2 yr) [kWh/m2 yr]
- Annual operational CO2e emissions (lb CO2e/ft2 yr) [kg CO2e/m2 yr]
- Total net embodied carbon (lb CO2e/ft2) [kg CO2e/m2]
- Water usage (gal/ft2 yr) [l/m2 yr]
- Thermal comfort: targets and design approach
- Daylighting: targets and design approach
- IAQ: targets and design approach
- Estimated construction cost($/ft2, exclusive of site acquisition and design costs) [$/m2]
- Other performance metrics considered pertinent by the design team
| return to top
Design Narrative
Teams will be expected to provide a design narrative that provides insights into the integrated design process and decisions leading to the final design proposal. In particular, the competition jurors will be interested in the progression of energy, carbon, and water performance as the proposal evolved, how best practices for indoor air quality (including consideration of health and wellness) were incorporated, and how thermal, visual, and acoustical comfort were addressed.
| return to top

Contextual Information
Background information on the Astrodome, including original drawings, can be found here.
Evaluation Criteria
| EVALUATION CRITERIA |
|
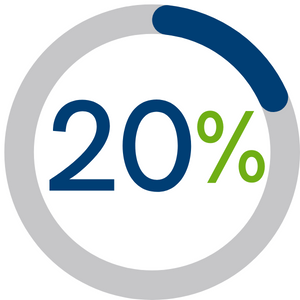
| 1. Demonstrating the impact of analysis on the design process |
20% |
| 2. Demonstrating how low-energy and low-carbon results were achieved |
20% |
| 3. Demonstrating how intended indoor environmental quality was achieved |
20% |
| 4. Innovation in design and analysis approach |
20% |
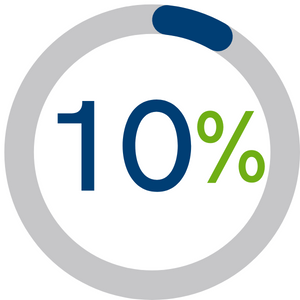
| 5. Clarity of workflow |
10% |
| 6. Effectiveness of presentation |
10% |
|

-
|
Demonstrating the impact of analysis on design results
Presentation materials clearly show that analysis was used to incrementally inform design decisions in a way that allowed the team to achieve its explicitly-stated design criteria
|
 |
|

-
|
Demonstrating how low-energy and low-carbon results were achieved
Presentation materials clearly show how operational energy and embodied carbon targets were established and how the design-analysis process supported reaching those targets
|
 |
|

-
|
Demonstrating how intended indoor environmental quality was achieved
Presentation materials clearly show how indoor environmental quality design criteria were established and how the design-analysis process supported reaching those targets
|
 |
|

-
|
Innovation in design and in analysis approach
Presentation materials explain key areas of design innovation etc.) and important areas of innovation in analysis (unique or custom simulation routines, etc.)
|
 |
|

-
|
Clarity in workflow
Presentation materials explain the design-analysis process workflow, with an emphasis on analysis informing and iterating design decisions
|
 |
|

-
|
Effectiveness of presentation
The presentation materials (graphic and verbal) are clear, informative, and exciting
|
 |
| return to top
2023 LowDown Showdown Judges
|

Christina Brown, Environmental Performance Specialist, Kohn Pedersen Fox, New York, NY
Christina X. Brown is a graduate of Carnegie Mellon University with a Bachelor of Architecture and Master of Science in Sustainable Design, currently working at Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates in New York City as an environmental performance specialist.
|

Keith Aaron Simon, FAIA, BCxP, Terracon, Austin, TX
An expert in building enclosure technology, Keith Simon addresses the critical and often unmet need for ensuring and improving building performance, resilience, and durability by guiding design teams, educating future architects, and facilitating interdisciplinary exchange.
|

Ladan Ghobad, Ph.D., Associate, ENERlite Consulting, Sacramento, CA
Dr. Ghobad is a building scientist and building performance simulation specialist with a Ph.D. degree in sustainable design; her practice focuses on energy modeling, daylighting, comfort, and thermal performance in buildings.
|
Important Dates
- August 14 | Deliverables Due
- Results Spreadsheet
- One Page Narrative
- Poster
- September 4 | PowerPoint Presentations Due
| return to top