ASHRAE Decarb: Events | About CEBD | Awards & Recognition | Positions | Recommendations | Commitments
ASHRAE
 | >> View the sessions relating to decarbonization
| >> View the sessions relating to decarbonization

Center of Excellence for Building Decarbonization (CEBD)
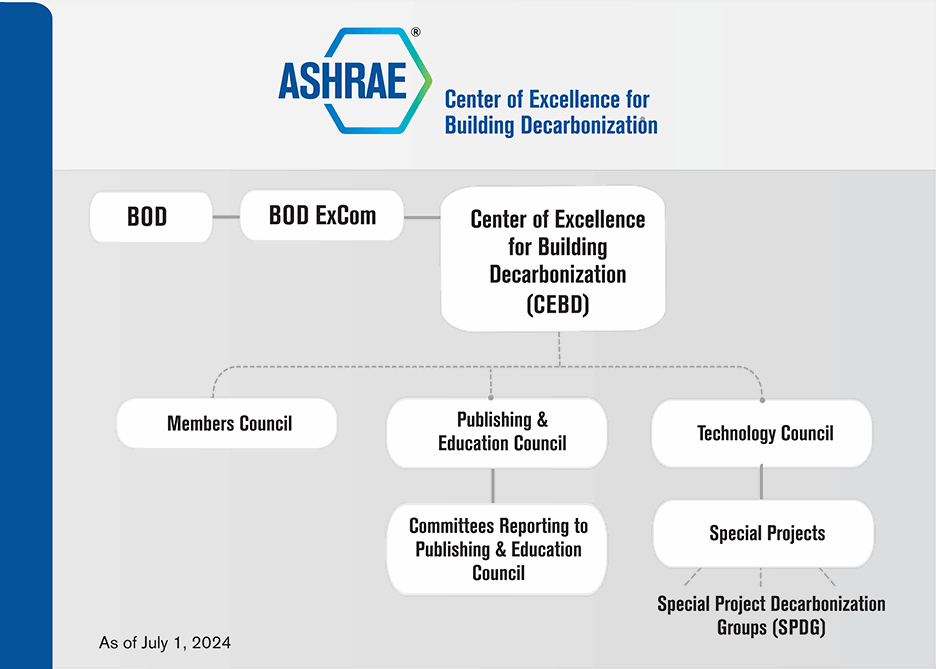
The CEBD will take a leading role in a number of strategic activities. The following is a summary of primary activities where the CEBD will take on a leading role.
- Strategy. Provide strategic direction for ASHRAE building decarbonization activities and work with the Planning Committee to incorporate appropriate goals into the Society strategic plan. ASHRAE’s building decarbonization strategy will be updated annually to keep up with the rapid pace of change in this area. Develop, lead and/or participate in strategic initiatives, generally with partner organizations, that accelerate and advance building decarbonization on a global basis.
- Thought Leadership. Monitor future issues and trends and publicize ASHRAE’s decarbonization work globally to establish ASHRAE’s leadership position, in partnership with Marketing.
- Collaboration. Coordinate joint initiatives, events, and projects with other U.S. and international organizations whose work is complementary to ASHRAE’s building decarbonization activities.
- Public Advocacy. Work with Government Affairs to provide reliable technical information on decarbonization to policymakers, media, and the public.
Working with over 100 volunteers from around the world, the 2024-2025 priority projects include: decarbonization guides, educational seminars and courses, the Certified Decarbonization Professional (CDP) certification, research projects, website material, and collaboration with industry partners.
2024-25 CEBD Voting Members
Kent Peterson, P.E., Chair
Blake Ellis, P.E., Vice Chair
Ghina Annan
Carrie Brown, Ph. D.
Luke Leung, P.E.
Bing Liu
Clay Nesler
Rajan Rajendran, Ph. D.
Stet Sanborn
Ginger Scoggins, P.E.
2024-25 CEBD Non-Voting Members
Kayleigh Houde, MEP 2040 Liaison
Bill McQuade, P.E., Members Council Liaison
Jeremy Smith, P.E., Technology Council Liaison
Costas Balaras, P.E., Ph. D., Technology Council Liaison
Stephanie Reiniche, Staff Liaison
CEBD Plan Progress

| Return to Top